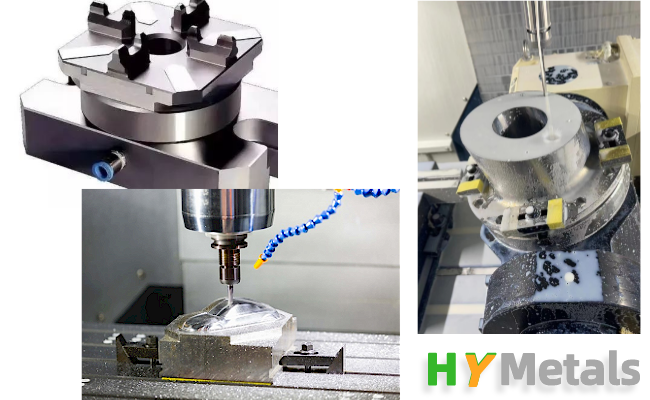
CNC machining is a precision manufacturing process that requires high-quality fixtures to accurately position the parts being machined. The installation of these fixtures is critical to ensuring that the machining process produces parts that meet the required specifications.
An important aspect of fixture installation is clamping. Clamping is the process of securing a part to a fixture to hold it in place during machining. The clamping force applied must be sufficient to prevent the part from moving during machining, but not so great that it deforms the part or damages the fixture.
There are 2 main purpose for clamping, one is accurate positioning, one is to protect the products.
The quality of the clamping method used can significantly affect the accuracy of the machined part. The clamping force should be evenly distributed over the part to prevent deformation, and the fixture should be designed to provide adequate support for the part.
There are several clamping methods for CNC machining operations, including manual clamping, hydraulic clamping, and pneumatic clamping. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, depending on the application and the type of part being machined.
Manual clamping is the simplest and most common clamping method used in CNC machining. It involves tightening a bolt or screw with a torque wrench to secure a part to a fixture. This method is suitable for most machining operations, but may not be suitable for parts with complex shapes or those made of delicate materials.
Hydraulic clamping is a more advanced clamping method that uses high pressure fluid to generate clamping force. This method is suitable for operations that require high clamping forces or that require precise control of clamping forces.
Pneumatic clamping is similar to hydraulic clamping, but instead of fluid, it uses compressed air to generate the clamping force. This method is most often used on smaller parts or where quick changeovers are required.
Regardless of the clamping method used, proper loading of the part into the fixture is also essential to ensuring accuracy. Parts should be positioned in the fixture so that they are fully supported and clamped in place. Any shifting or shifting of the part during machining can result in inaccurate cuts and dimensions.
A key factor in determining the best clamping and loading method is the required tolerances of the part being machined. Tolerances are the allowable deviations in size, shape, or other dimensions of a part. The tighter the tolerances, the more care needs to be taken in fixture design, clamping and part positioning.
In short, the impact of clamping on the accuracy of CNC machined parts cannot be overemphasized. Proper clamping and loading are necessary to achieve required tolerances and produce high quality parts. The choice of clamping method depends on the specifics of the application and the type of part being machined. Therefore, designers and manufacturers must carefully understand the requirements of each machining operation and select the appropriate clamping and loading techniques to ensure that the final product meets the required quality and precision standards.
Post time: Mar-29-2023