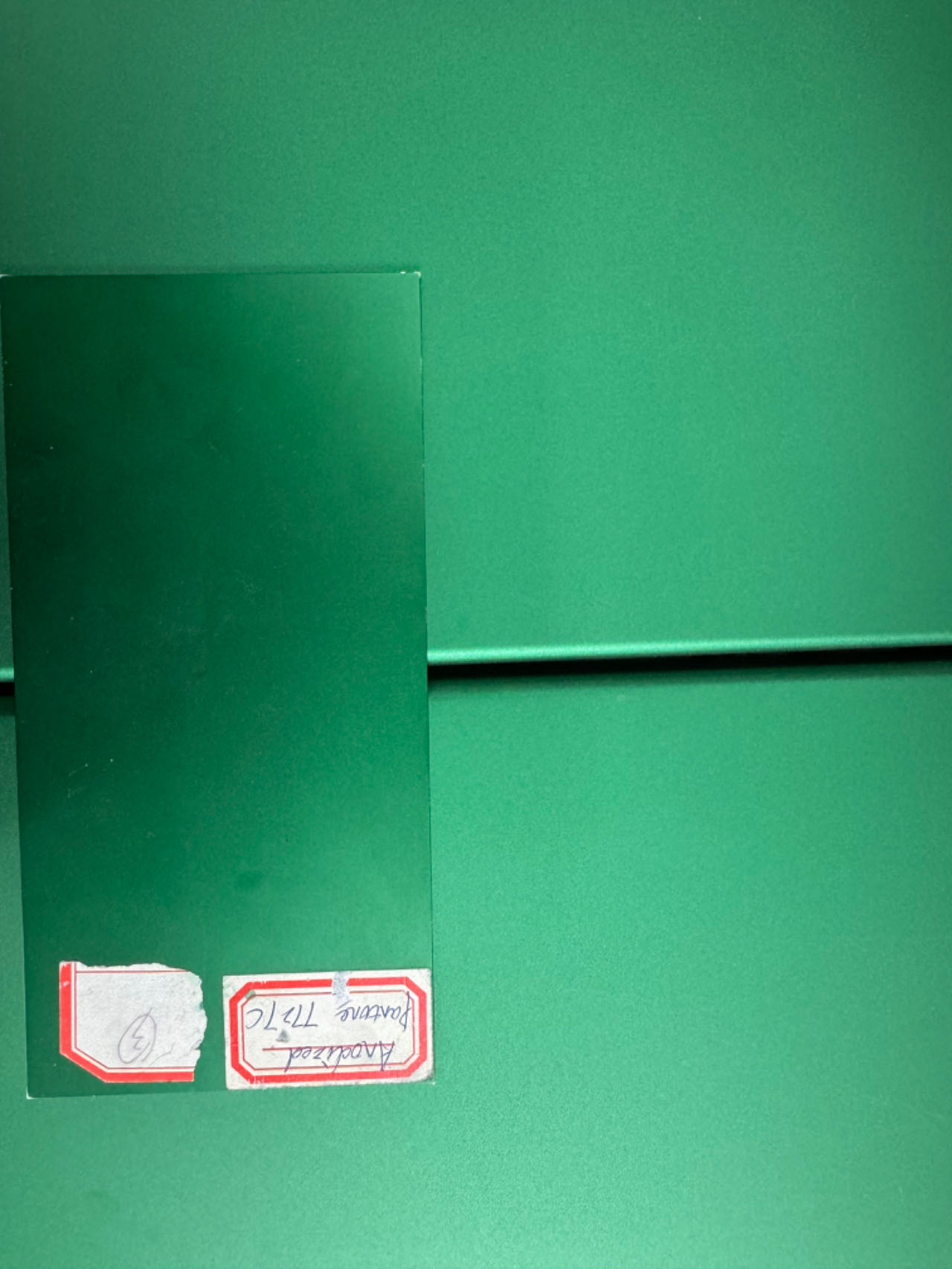
Aluminum anodizing is a widely used process that enhances the properties of aluminum by forming a protective oxide layer on its surface. The process not only provides corrosion resistance but also colors the metal.
However, a common problem encountered during aluminum anodization is color variation that occurs even within the same batch. Understanding the reasons behind this variation and implementing effective controls are critical to achieving a consistent and high-quality anodized product.
Color changes in aluminum anodization can be attributed to a variety of factors.
One important reason is the inherent variability of aluminum surfaces. Even within the same batch, differences in grain structure, alloy composition and surface defects can cause variations in the effect of the anodizing process on the metal.
In addition, the anodizing process itself causes changes in the thickness of the oxide layer due to factors such as current density, temperature, and chemical composition of the anodizing solution. These changes in oxide layer thickness directly affect the perceived color of anodized aluminum.
In addition, environmental conditions and process parameters, such as bath agitation, temperature control, and anodization time, can also cause color differences. Even small fluctuations in these parameters can lead to inconsistent results, especially in large-scale anodizing operations where maintaining uniformity becomes challenging.
In order to control color changes in aluminum anodization, a systematic approach must be taken to address the root cause. Implementing strict process control and monitoring systems is critical.
First and foremost, proper preparation of aluminum surfaces can reduce initial variability by ensuring uniformity through processes such as mechanical polishing and chemical cleaning.
Additionally, optimizing anodizing process parameters such as voltage, current density, and time will help achieve consistent oxide layer thickness and thus uniform coloration. Using a high-quality anodizing tank with stable chemical composition and an effective filtration system helps maintain the integrity of the anodizing solution and reduce the impact of impurities that can cause color deviations.
Additionally, regular maintenance and calibration of anodizing equipment and maintaining stable environmental conditions within anodizing facilities are critical to minimizing process-induced variations.
Using advanced analytical techniques, such as spectrophotometry, to measure color and thickness changes on anodized surfaces can help identify and correct inconsistencies. By integrating these measurement tools into quality control processes, manufacturers can make informed decisions to adjust process parameters and achieve color uniformity.
Additionally, employing statistical process control (SPC) methods to monitor and analyze production data can help identify trends and changes, allowing proactive adjustments to the anodization process. Improving employee training and creating standardized operating procedures will also help reduce color variation by ensuring that all personnel involved in the anodizing process follow consistent protocols.
In summary, achieving uniform coloration in aluminum anodization, even within the same batch, requires a holistic approach that addresses the multifaceted factors that contribute to color variation. By focusing on surface treatment, process optimization, quality control and employee training, HY Metals can effectively control and minimize color differences, ultimately delivering high-quality anodized products that meet customer expectations. Through continuous improvement and a commitment to process excellence, the issue of color change in aluminum anodization can be effectively managed to produce consistent and beautiful anodized aluminum products.
In our production practice, lots of customers just give a color number or electronic pictures to show us what color effect they want. That’s not enough to get a critical color. We usually trying to get more information to match the color as close as possible.
Post time: Feb-24-2024