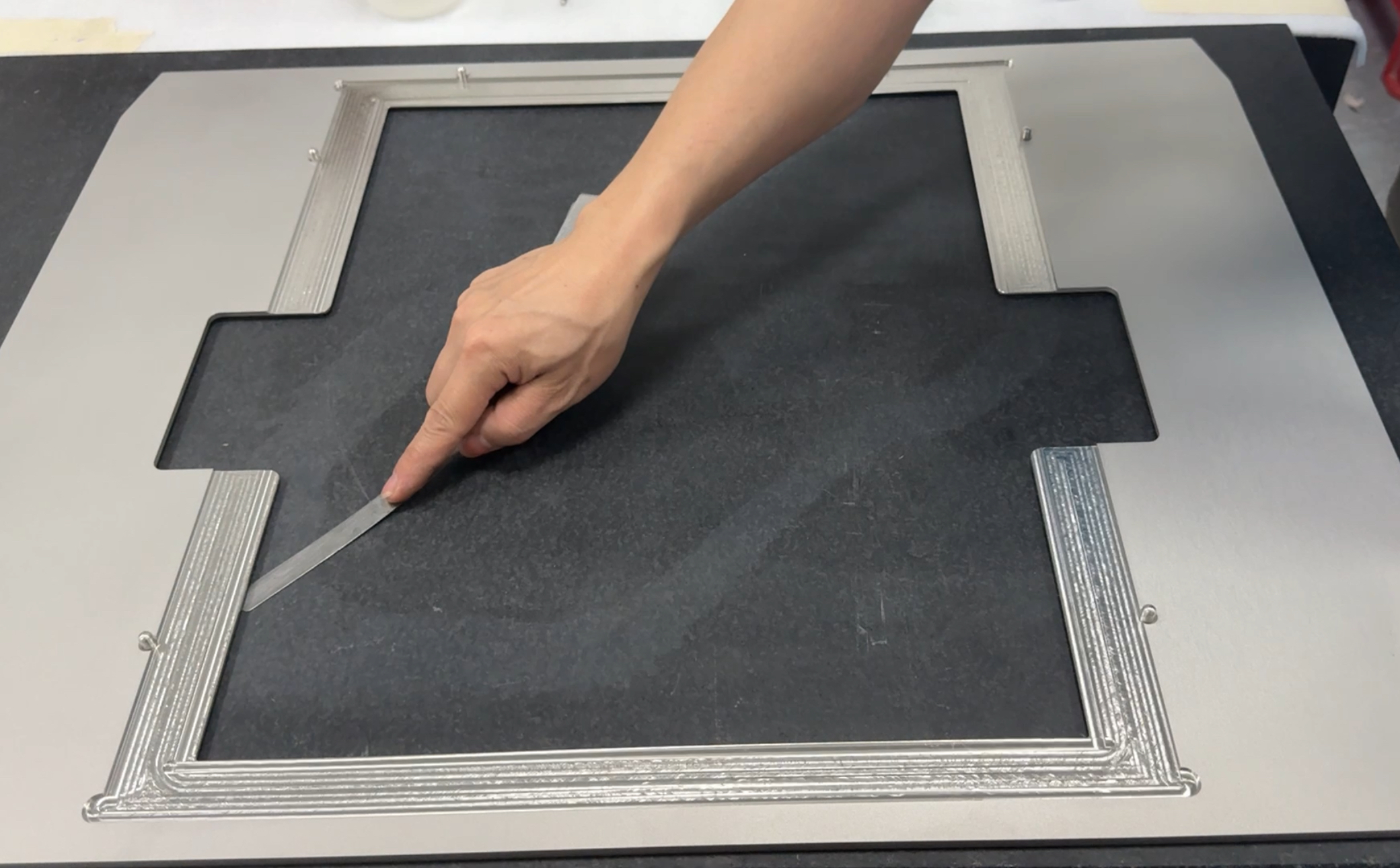
Flatness is a critical geometric tolerance in machining, especially for sheet metal and CNC machining processes. It refers to the situation where all points on a surface are equidistant from a reference plane.
Achieving flatness is critical for the following reasons:
1. Functional Performance: Many components must fit together precisely. If the parts are not flat, it can cause misalignment and affect the overall functionality of the assembly.
2. Load Distribution: Flat surface ensures even load distribution. Uneven surfaces can cause stress concentrations that can lead to premature component failure.
3. Aesthetic Quality: In industries where appearance is important, such as automotive and consumer electronics, flatness helps improve the visual appeal of the product.
4. Assembly Efficiency: Uneven parts can complicate the assembly process, resulting in increased labor costs and time.
5. Precision for further machining: Flatness is often a prerequisite for subsequent machining operations such as drilling or milling, where a flat surface is necessary to obtain accurate results.
Maintain flatness during processing
Achieving and maintaining flatness during machining requires careful planning and execution. Here are some strategies:
1. Material Selection: Choose materials that are not easy to warp or deform during processing. Metals with lower coefficients of thermal expansion are generally preferred.
2. Correct Fixtures: Use appropriate fixtures to securely hold the workpiece during machining. This minimizes movement and vibration that can cause warping.
3. Controlled machining parameters: Optimize cutting speed, feed and depth of cut. Excessive heat generated during processing can cause thermal expansion and warping.
4. Sequential Machining: If possible, machine parts in stages. This allows material to be removed in a controlled manner, reducing the risk of deformation.
5. Post-processing treatment: Consider stress relief processes such as post-processing annealing or normalizing to eliminate internal stress that may cause warpage.
6. Use of Flat Reference Surface: Regularly check and calibrate machine tools to ensure they are running on a flat reference surface.
Check flatness
To ensure that machined parts meet flatness specifications, appropriate inspection techniques must be used:
1. Visual Inspection: A simple visual inspection can sometimes reveal obvious flatness issues, such as gaps under a part or light passing through.
2. Ruler Method: Place a precision ruler on the surface and use a feeler gauge to measure any gaps. This method is very effective for quick inspection.
3. Dial indicator: A dial indicator can be used to measure the flatness deviation of the entire surface. This method provides more precise measurements.
4. Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM): For high-precision applications, a CMM can be used to measure the flatness of a surface by taking multiple points and calculating the deviation from a reference plane.
5. Optical Plane Method: This involves using an optical plane and monochromatic light to check flatness. Interference patterns can indicate deviations.
6. Laser Scanning: Advanced laser scanning technology provides detailed surface maps, allowing for a comprehensive analysis of flatness.
In conclusion
Flatness is an important aspect of processing, affecting functionality, aesthetics and assembly efficiency. By understanding its importance and implementing strategies to maintain and inspect flatness, HY METALS can ensure the production of high-quality components that meet tight tolerances. Regular inspections and compliance with processing best practices will improve product performance and customer satisfaction.
HY Metals provide one-stop custom manufacturing services including sheet metal fabrication and CNC machining, 14 years experiences and 8 fully owned facilities.
Excellent Quality control, short turnaround, great communication.
Send your RFQ with detailed drawings today. We will quote for you ASAP.
WeChat:na09260838
Tell:+86 15815874097
Email:susanx@hymetalproducts.com
Post time: Oct-10-2024