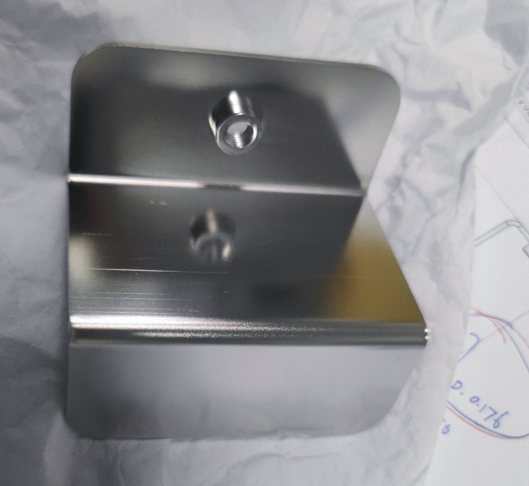
Stainless steel sheet metal parts can be given a variety of surface treatments to enhance their appearance, corrosion resistance, and overall performance. Here are some common surface treatments and their advantages and disadvantages:
1.Passivation
- DESCRIPTION: A chemical treatment that removes free iron and enhances the formation of a protective oxide layer.
- Advantage:
- Improved corrosion resistance.
- Improve surface cleanliness.
- Shortcoming:
- May require specific conditions and chemicals.
- Not a substitute for correct material selection.
2. Electropolishing
-DESCRIPTION: An electrochemical process that removes a thin layer of material from a surface, resulting in a smooth surface.
- advantage:
- Enhanced corrosion resistance.
-Reduced surface roughness, easier to clean.
- shortcoming:
- May be more expensive than other treatments.
- May not be available on all stainless steel grades.
3. Brushing (or satin finish)
-DESCRIPTION: A mechanical process that uses an abrasive pad to create a uniformly textured surface.
- advantage:
- Aesthetics with a modern look.
- Hides fingerprints and minor scratches.
- shortcoming:
- Surfaces may still be susceptible to corrosion if not properly maintained.
- Requires regular cleaning to maintain appearance.
4. Polish
- DESCRIPTION: A mechanical process that produces a shiny reflective surface.
- advantage:
- High aesthetic appeal.
- Good corrosion resistance.
- shortcoming:
- More prone to scratches and fingerprints.
- Requires more maintenance to maintain shine.
5. Oxidize (black) or QPQ
QPQ Steel and Stainless Steel Surface Treatment
QPQ (Quenched-Polished-Quenched) is a surface treatment process that enhances the properties of steel and stainless steel. It involves a series of steps to improve wear resistance, corrosion resistance and surface hardness.
Process overview:
1. Quenching: Steel or stainless steel parts are first heated to a specific temperature and then rapidly cooled (quenched) in a salt bath or oil. This process hardens the material.
2.Polishing: The surface is then polished to remove any oxides and improve the surface finish.
3. Secondary Quenching: Parts are usually quenched again in a different medium to further increase the hardness and form a protective layer.
Advantage:
-Enhanced Wear Resistance: QPQ significantly improves the wear resistance of treated surfaces, making it suitable for high friction applications.
- Corrosion Resistance: This process creates a hard protective layer that enhances corrosion resistance, especially in harsh environments.
-Improved Surface Finish: The polishing step produces a smoother surface, which is beneficial for both aesthetic and functional purposes.
-Increase Hardness: Treatment increases surface hardness, which can extend the service life of components.
Shortcoming:
- Cost:The QPQ process can be more expensive than other surface treatments due to complexity and equipment required.
- Certain alloys only: Not all steel and stainless steel grades are suitable for QPQ processing; compatibility must be evaluated.
- Potential Warping: The heating and quenching process may cause dimensional changes or warping in some parts, requiring careful control and design consideration.
QPQ is a valuable surface treatment that improves the performance of steel and stainless steel components, especially in applications requiring high wear and corrosion resistance. However, cost, material compatibility, and potential deformation should be considered when deciding on this treatment.
6. Coating (e.g. powder coating, paint)
- Description: Applies a protective layer on stainless steel surfaces.
- advantage:
- Provides additional corrosion resistance.
- Available in a variety of colors and finishes.
- shortcoming:
- Over time, the coating may chip or wear away.
- May require more maintenance than untreated surfaces.
7. Galvanized
- DESCRIPTION: Coated with a layer of zinc to prevent corrosion.
- advantage:
- Excellent corrosion resistance.
- Cost effective for large parts.
- Shortcoming:
- Not suitable for high temperature applications.
- Can change the appearance of stainless steel.
8. Laser Marking or Etching
- DESCRIPTION: Use a laser to engrave or mark surfaces.
- advantage:
- Permanent and precise marking.
- No impact on material properties.
- shortcoming:
- Marking only; does not enhance corrosion resistance.
- Can be costly for large-scale applications.
In conclusion
The choice of surface treatment depends on the specific application, desired aesthetics and environmental conditions. Each treatment method has its own advantages and disadvantages, so these factors must be considered when selecting the appropriate treatment method for stainless steel sheet metal parts.
Post time: Oct-05-2024